As Comparing REITs and Dividend ETFs Like JEPI takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with casual formal language style into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
When delving into the realm of real estate investment trusts (REITs) and dividend exchange-traded funds (ETFs) like JEPI, a fascinating journey unfolds revealing the nuances and intricacies of these popular investment vehicles.
Introduction to REITs and Dividend ETFs like JEPI
REITs, or Real Estate Investment Trusts, are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate across a range of property sectors. They are required to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends, making them attractive for income-seeking investors.
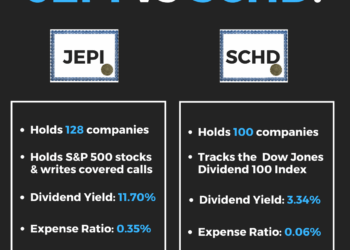
On the other hand, Dividend ETFs like JEPI (JPMorgan Equity Premium Income ETF) are exchange-traded funds that focus on investing in dividend-paying stocks with the goal of providing a steady income stream to investors while also offering potential for capital appreciation.
Key Differences Between REITs and Dividend ETFs
- Ownership Structure: REITs are companies that own and operate real estate properties, while Dividend ETFs like JEPI own a diversified portfolio of dividend-paying stocks.
- Income Generation: REITs generate income through rental payments and property appreciation, while Dividend ETFs generate income through dividends paid by the stocks in their portfolio.
- Risk Exposure: REITs are more directly exposed to the real estate market and economic conditions, while Dividend ETFs diversify risk across multiple companies and sectors.
- Tax Treatment: REIT dividends are taxed as ordinary income, while dividends from Dividend ETFs may qualify for lower tax rates depending on the holding period and individual tax situation.
Characteristics of REITs and Dividend ETFs
When it comes to investing in real estate investment trusts (REITs) and dividend exchange-traded funds (ETFs) like JEPI, there are distinct characteristics that set them apart. Let's delve into the key features of each investment option.
Characteristics of REITs
REITs are known for their unique characteristics, including:
- Dividends: REITs are required to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends, making them attractive for income-seeking investors.
- Risks: REITs are subject to risks such as interest rate fluctuations, economic downturns, and property market volatility, which can impact their performance.
- Liquidity: While REITs are traded on major stock exchanges, their liquidity can vary depending on the specific REIT and market conditions.
Characteristics of Dividend ETFs like JEPI
Dividend ETFs like JEPI offer investors a different set of characteristics, such as:
- Diversification: Dividend ETFs provide investors with exposure to a diversified portfolio of dividend-paying stocks, reducing single-stock risk.
- Expense Ratios: Dividend ETFs typically have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds, making them cost-effective investment options.
- Performance Tracking: Dividend ETFs like JEPI track specific dividend indexes or strategies, allowing investors to easily monitor and assess their performance over time.
Performance Comparison
When comparing the historical performance of REITs and Dividend ETFs like JEPI, it is essential to consider the specific period under analysis and the factors influencing their performance.
Historical Performance Analysis
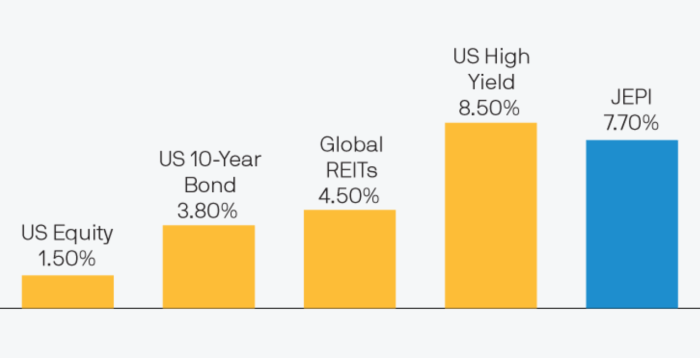
- REITs have shown strong performance in the past, often outperforming the broader market in terms of total returns.
- Dividend ETFs like JEPI have also delivered consistent returns to investors, focusing on income generation through dividend payments.
- Over a specific period, the performance of REITs and Dividend ETFs may vary based on market conditions and economic factors.
Factors Influencing Performance
- Interest rates: Changes in interest rates can impact the performance of REITs, as they are sensitive to borrowing costs. Dividend ETFs may also be affected, but to a lesser extent.
- Real estate market trends: REITs are directly influenced by the real estate market conditions, while Dividend ETFs like JEPI may be more diversified across sectors.
- Dividend policies: The dividend payout ratios and growth rates of companies within Dividend ETFs can affect their overall performance compared to REITs.
Market Conditions Impact
- In a low-interest-rate environment, REITs may perform well due to lower borrowing costs, while Dividend ETFs might face challenges in generating higher yields.
- During economic downturns, REITs may experience a decline in property values, impacting their performance, whereas Dividend ETFs could benefit from stable dividend payments from diverse holdings.
- Market volatility can affect both REITs and Dividend ETFs differently, depending on the underlying assets and strategies employed by each investment option.
Risk Assessment
Investing in REITs and Dividend ETFs like JEPI comes with its own set of risks that investors need to consider. Let's evaluate the risk profiles of both investment options to understand the potential challenges and rewards they offer.
Risks associated with REITs
REITs are susceptible to various risks, including interest rate risks, market risks, and sector-specific risks.
- Interest rate risks: REITs are sensitive to changes in interest rates, as higher rates can lead to increased borrowing costs and lower property valuations.
- Market risks: Fluctuations in the real estate market can impact the performance of REITs, making them vulnerable to economic downturns or shifts in investor sentiment.
- Sector-specific risks: Different types of REITs (e.g., residential, commercial, healthcare) face unique challenges related to their specific industry, such as changing demographics or regulatory changes.
Risk profile of Dividend ETFs like JEPI
Dividend ETFs offer a different risk profile compared to individual REITs.
- Market volatility: Dividend ETFs are subject to market volatility, which can lead to fluctuations in their share prices based on broader market movements.
- Credit risk: The creditworthiness of the companies held within the ETF can impact its performance, with higher credit risk potentially leading to lower dividend payments.
- Diversification benefits: Dividend ETFs provide diversification benefits by holding a basket of dividend-paying stocks, reducing the impact of individual company risks.
Risk-return tradeoff between REITs and Dividend ETFs
When comparing the risk-return tradeoff between REITs and Dividend ETFs, investors need to consider their risk tolerance and investment goals.
- REITs typically offer higher potential returns but come with higher risks due to their direct exposure to real estate markets.
- Dividend ETFs like JEPI provide a more diversified approach to income investing, offering potentially lower returns but with reduced risk through a portfolio of dividend-paying stocks.
Tax Implications
When it comes to investing in REITs and Dividend ETFs like JEPI, understanding the tax implications is crucial for maximizing returns and managing your overall investment strategy. Let's delve into how these investments are taxed and any advantages or disadvantages that investors should be aware of.
Tax Treatment of REITs Dividends
- REIT dividends are typically taxed at ordinary income tax rates, rather than the lower qualified dividend tax rates that apply to many other types of dividends.
- Investors should be prepared for potentially higher tax obligations when receiving dividends from REIT investments.
Taxation of Dividend ETFs vs. Direct REIT Investments
- Dividend ETFs like JEPI offer a diversified portfolio of dividend-paying stocks, including REITs, which can provide tax efficiency through the structure of the ETF.
- Dividend ETFs are taxed based on the underlying assets held within the fund, which can result in more favorable tax treatment compared to holding individual REIT stocks directly.
Tax Advantages and Disadvantages of REITs vs. Dividend ETFs
- One advantage of holding REITs directly is the potential for pass-through tax treatment, where a portion of the dividends may be considered return of capital and not immediately taxable.
- On the other hand, Dividend ETFs like JEPI may offer greater diversification and potentially more tax-efficient distributions, especially for investors seeking exposure to dividends from various sectors.
- Investors should weigh the tax implications of both options based on their individual tax situation and investment goals.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the comparison between REITs and Dividend ETFs like JEPI sheds light on the diverse characteristics, performance metrics, and risk profiles of these two investment options. This insightful analysis serves as a valuable guide for investors seeking to navigate the complex terrain of the financial markets with confidence and knowledge.
FAQ
What are the tax implications of investing in REITs?
REIT dividends are typically taxed as ordinary income, but investors can benefit from certain tax advantages such as deductions for dividends paid.
How do Dividend ETFs like JEPI differ from direct REIT investments in terms of taxation?
Dividend ETFs are taxed at the capital gains rate, which may offer tax advantages compared to direct REIT investments that are taxed as ordinary income.
What factors influence the performance of REITs and Dividend ETFs like JEPI?
Market conditions, interest rates, and sector-specific dynamics play a significant role in determining the performance of both REITs and Dividend ETFs.